Question 1
Which statement about the Sun and Earth is correct?
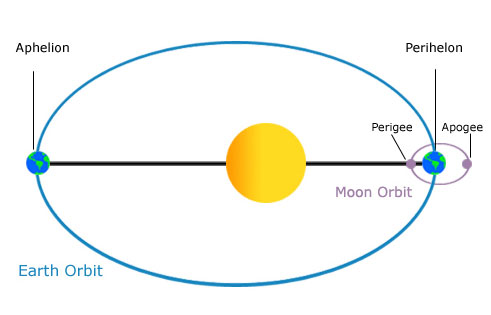
(b) Because the Sun is much more massive than Earth, the Moon experiences a stronger gravity from the Sun than from Earth.
(c) Their centre of mass is at the centre of the Sun.
(d) Their centre of mass is the midpoint between them.
Question 2
Seasons occur mainly because of
(a) Our changing distance from the Sun
(a) The self-rotation of Earth
(c) Earth’s axis being not perpendicular to its orbital plane
(d) The Moon’s gravitational influence
Question 3
The colour of a star is principally determined by
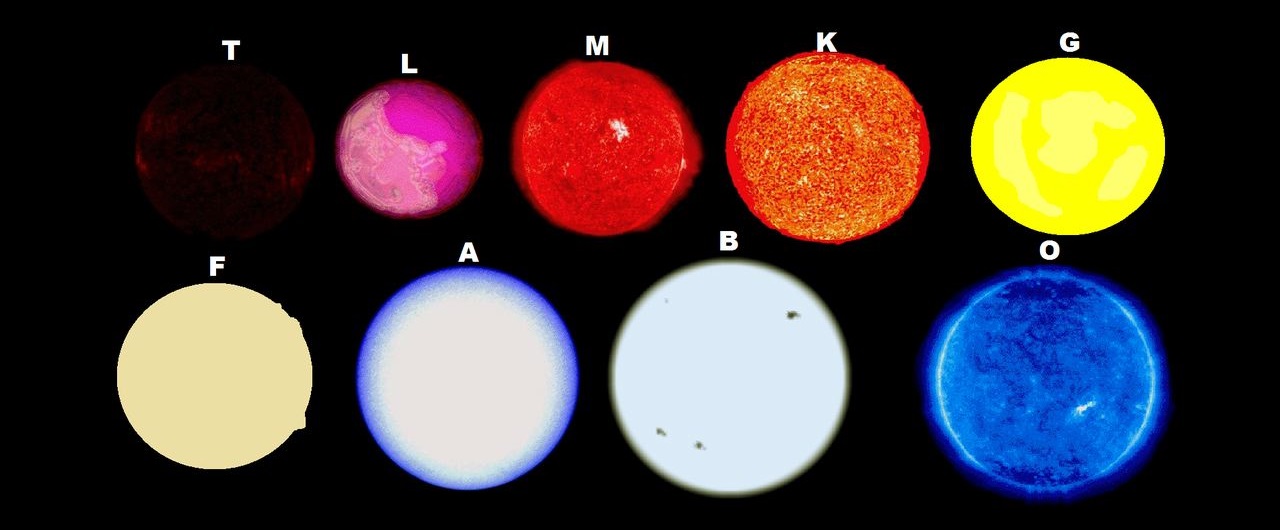
(a) Distance
(b) Chemical composition
(c) Size
(d) Surface temperature
Question 4
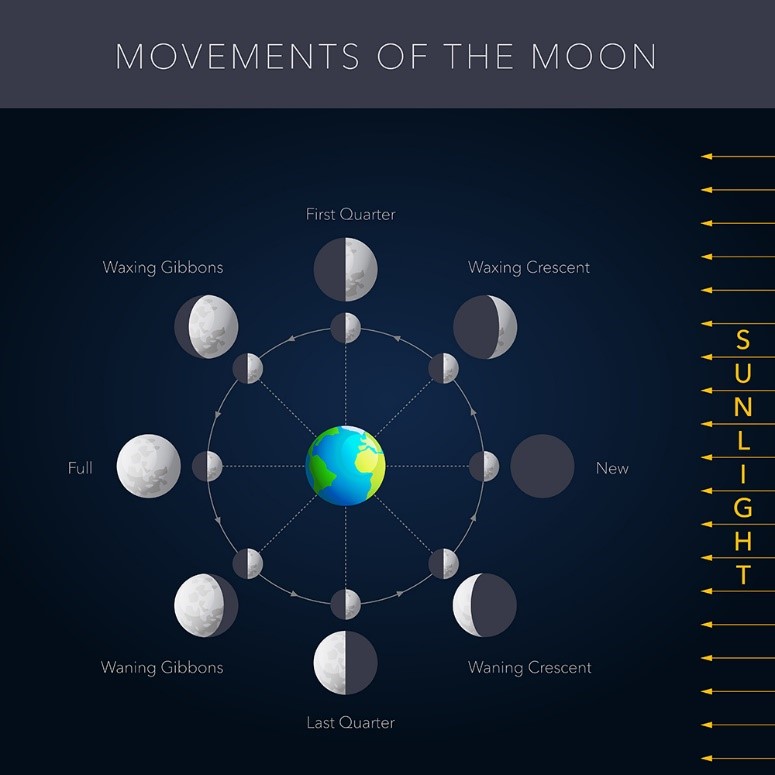
The Moon appears to show phases when observed from Earth caused by
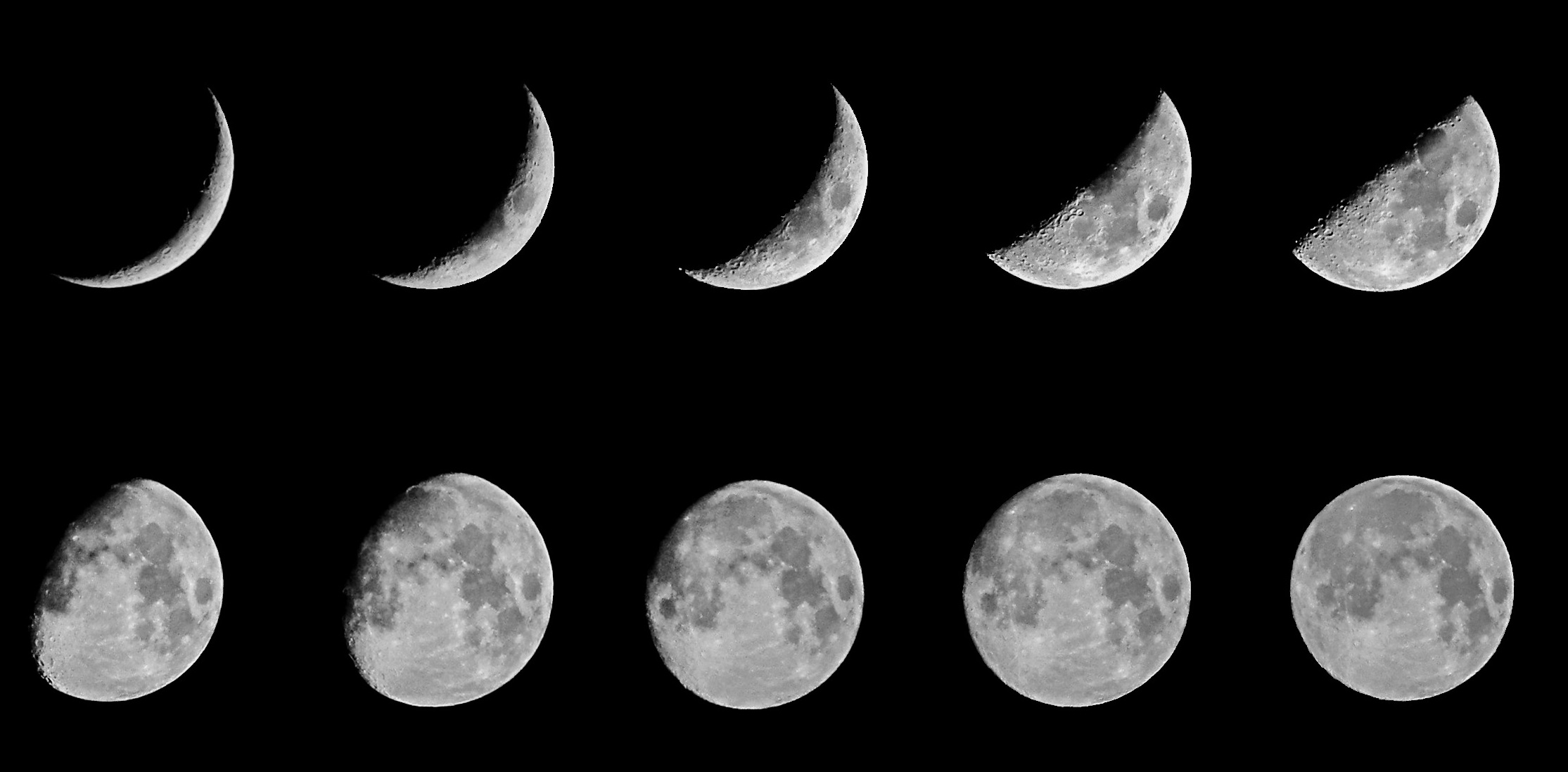

(a) Our viewing direction compared to the direction of sunlight
(b) The shadow of the Earth
(c) Its own irregular shape
(d) Its own shadow
Question 5
The Pleiades (Seven Sisters) is an open star cluster (see photo below), with more than 1000 stars. These are stars that were formed within the last 100 million years in the same nebula. Which of the following statements about the stars in the Pleiades are correct?

(a) II only
(b) III only
(c) I and II
(d) II and III
Question 6
Light from a distant galaxy is red shifted due to the expansion of the universe. In the photo below, a galaxy was observed with redshift 11, meaning that the wavelength of its light was stretched to become 12 times its original value. We are seeing the galaxy as it was 13.4 billion years ago. What are the distances to the galaxy today and when it emitted the light captured in the photograph?
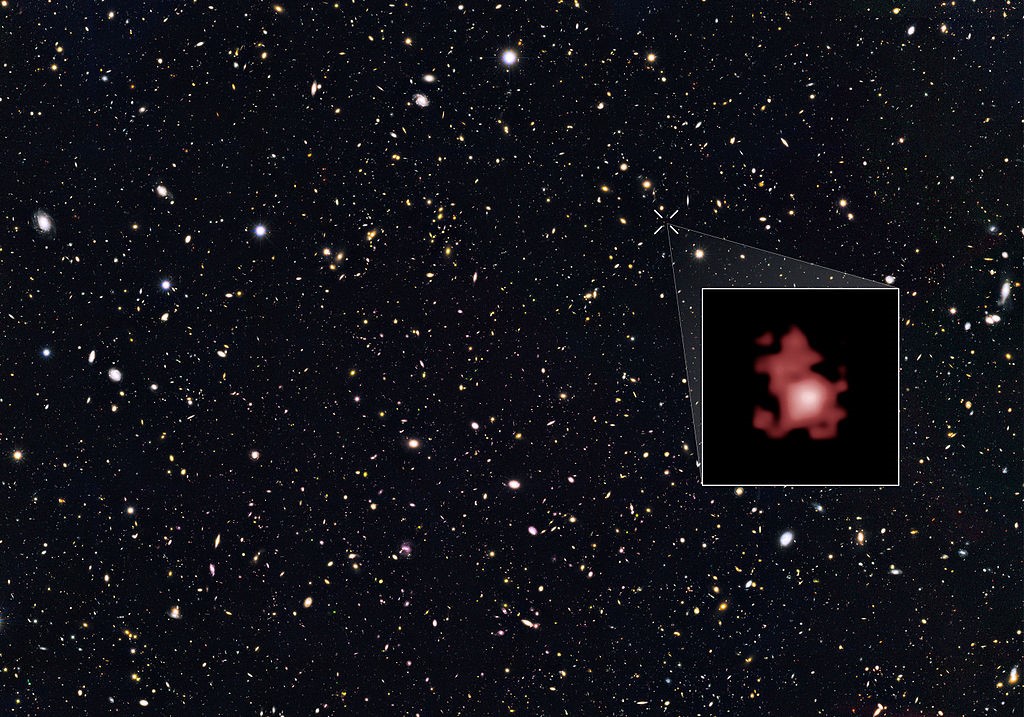

(a) 32 and 13.4 billion light years
(b) 13.4 and 2.7 billion light years
(c) 32 and 2.7 billion light years
(d) 13.4 and 1.1 billion light years
Answer
Question 1: (a) The gravitational attraction between them is sometimes stronger and sometimes weaker.
It is because the orbit of Earth is elliptical. The centre of mass is neither at the centre of the Sun nor the midpoint between them. The distance between the Sun and Earth is sometimes shorter and sometimes longer. Since the gravitational attraction is inversely proportional to the square of the distance, the attraction is sometimes stronger and sometimes weaker. Moreover, the Moon experiences a stronger gravity from Earth (not the Sun) because Earth is much closer to the Moon.
Question 2: (c) Earth’s axis being not perpendicular to its orbital plane
The effect of the changing distance between Earth and the Sun is not the major reason. The self-rotation of Earth and the Moon’s gravitational force are not related to seasons. We have seasons because there is a significant difference in the sunlight absorption between the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere. The difference is due to the tilted Earth’s axis of self-rotation.
Question 3: (d) Surface temperature
The colour of light emission depends on the surface temperature of a star. A hotter star would emit more blue light, followed by white, yellow, orange and a colder star would emit more red light. The following are some examples: -
|
Example star colours and corresponding approximate surface temperatures |
||
|
Star Colour |
Approximate Temperature |
Example |
|
Blue |
25,000 K |
Spica |
|
White |
10,000 K |
Vega |
|
Yellow |
6,000 K |
Sun |
|
Orange |
4,000 K |
Aldebaran |
|
Red |
3,000 K |
Betelgeuse |
Question 4: (a) Our viewing direction compared to the direction of sunlight
When the Moon orbits Earth, the relative position of Earth, the Moon and the Sun keep changing constantly, allowing observers from Earth to see the illuminated lunar surface from different directions, resulting in the changing appearances of the Moon.
Question 5: (a) II only
I is incorrect. The stars differ in their masses, which determine their ages. More massive and brighter stars will die first, leaving behind the less massive and dimmer ones. II is correct because they are formed from the same nebula. III is incorrect, as the stars will disperse after the cluster encounters other nebulae or stars as they orbit around Milky Way.
Question 6: (c) 32 and 2.7 billion light years
The image shows the galaxy as it was 13.4 billion years ago. Therefore, the light traveling distance of the galaxy is 13.4 billion light years. However, because of the expansion of the universe, the galaxy must be located much farther away now. The only answer that’s larger than 13.4 billion light years is 32 billion light years. So (i), (iii), and (iv) could be correct. If the present distance to the galaxy is 32 billion light years, and the redshift is 11, then the original distance is 32/12 ≈ 2.7 billion light years. So (iii) is correct.


